Time Traveling
Sometimes, you might end up in a situation where you want to go back to one of your previous commits. We can travel back in time and restore our codebase to be as it was at that time. Just one small catch, you can only go back in time and the changes cannot be undone. Before we do that, let’s check what our commit history looks like.
Git Log
This command shows a list of all the commits in the repository’s history.
git log
The output shows each commit in chronological order, along with the commit hash (the long string of numbers) and the commit message.
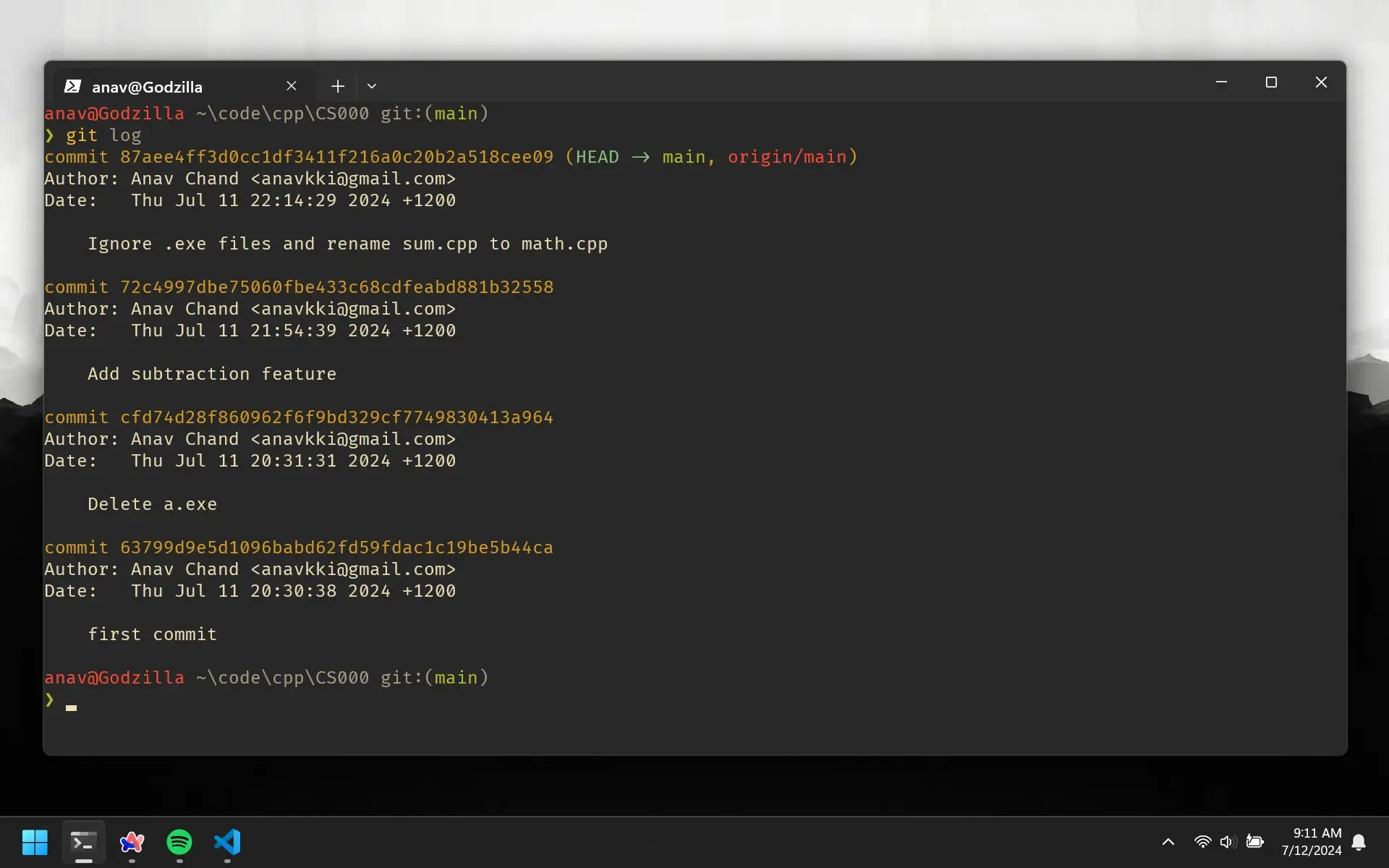
Git Head
Notice how HEAD is pointing to the most recent commit. This is the commit that our code is currently on. If we were to create another commit, the HEAD would point to that new commit.
commit 87aee... (HEAD -> main, origin/main)
The main is referring to the local branch and origin/main is referring to the branch on GitHub.
Git Reset
Say in our case, we want to go back to the commit when we created the repo and added the sum feature (the first commit). All we need is the commit hash for the first commit. Using the whole hash is not ideal, so let’s use the shorter version.
git log --oneline
This shows us a compact version of the commit hash and the commit message.
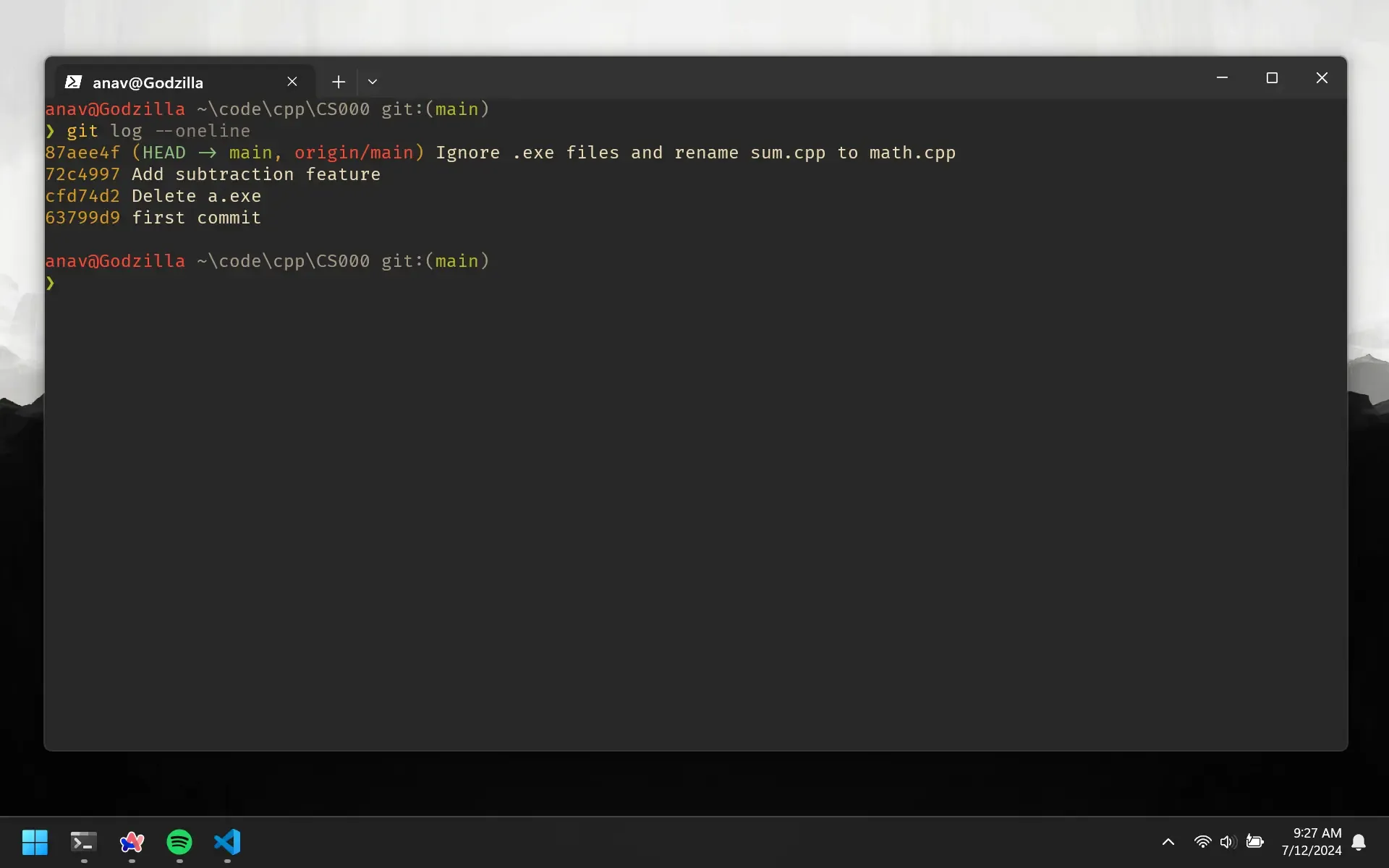
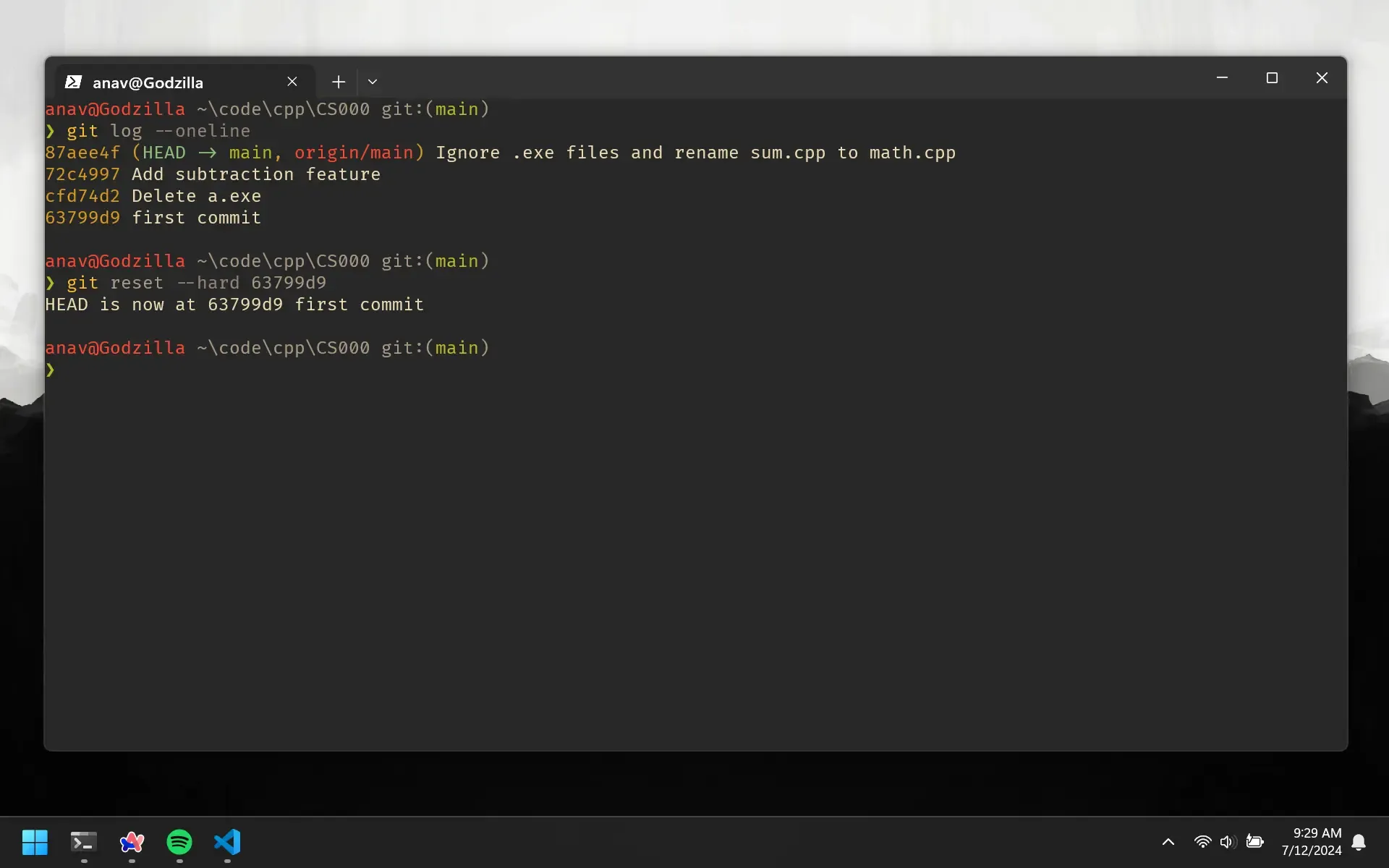
Let’s grab the hash for the first commit and use it to reset the HEAD to that commit.
git reset --hard 63799d9
This command resets the HEAD to the commit with the hash 63799d9. If you run git log again, you will see that the HEAD is now pointing to the first commit.
Quick Reset
In our case, we had 3 commits with no changes to our code. Let’s say you were trying to add a divide feature to the code and decided you wanted to undo it. If you did not commit those changes, you can simply do this:
git reset --hard HEAD
This command will discard all the uncommitted changes and reset the HEAD to the most recent commit.
Commit History
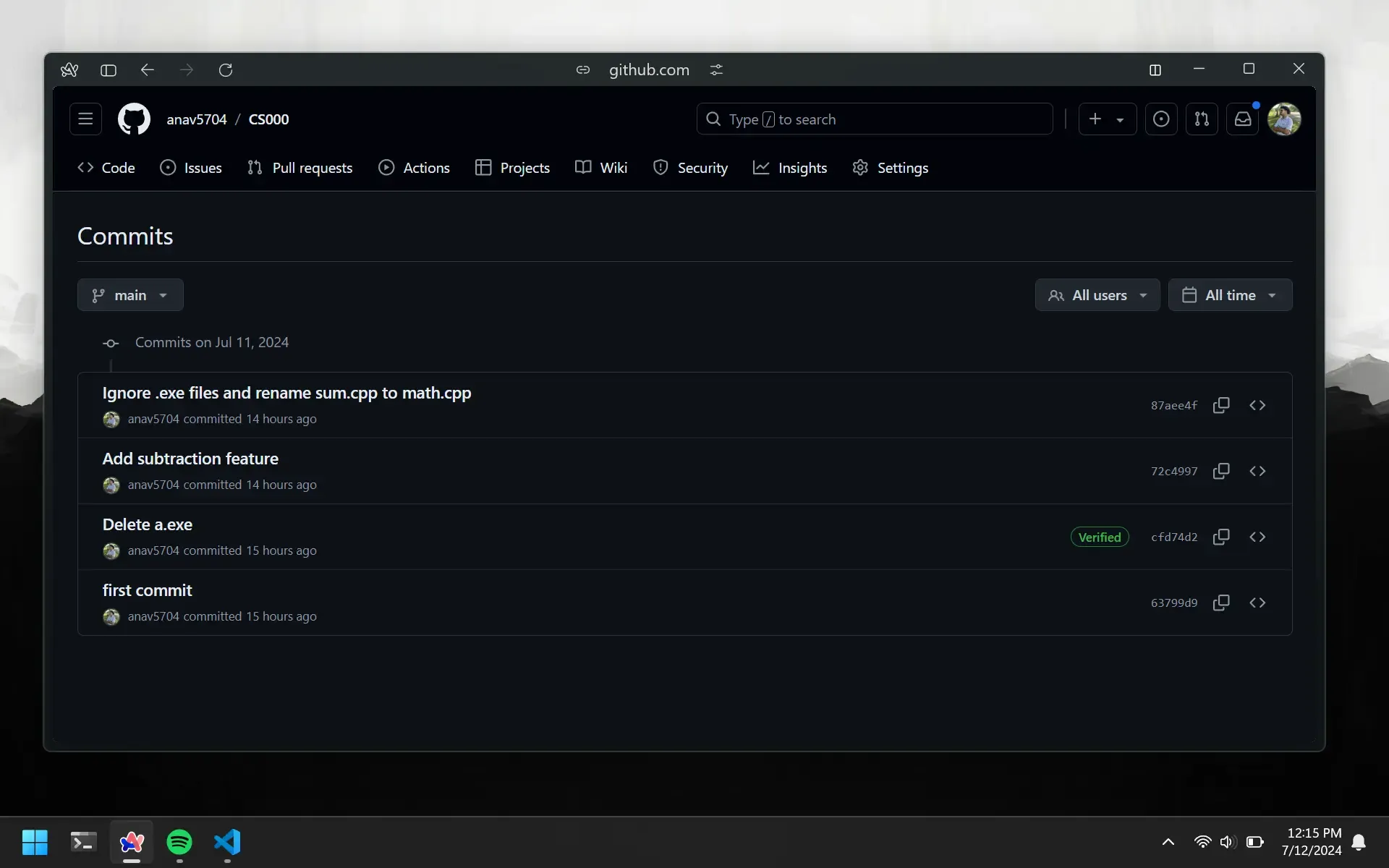
Every time you push your code to GitHub, it saves a snapshot of your code. GitHub will basically keep different versions of your code. This means you can view older versions of your code and see how it looked at a certain point in time. This is especially helpful when you delete things. You can go view a previous version of your code and see what it looked like before you deleted it.
In order to do so, first go to your repository on GitHub and click on the button Commits button under the green Code tab. This will show you all the commits in chronological order.
Once you are on the commits page, just pick the commit you want to go back to and click on the Browse files button. This is located beside the Copy button, which is beside the Commit hash.